A new finding indicates that sunlight is a threat to humanity rather than protect it. Sunlight is a source of vitamins, no doubt. however, the finding went on to emphasize that man faces a risk of cataract after long exposure to sun. The finding concludes that sunlight is public health risk. Ogbodo Ozioma Favour in this report looks at how sunlight causes severe eye disease.
Cataract Leading Cause of Blindness
According to recent data by Skipper Eye- Q International Eye Hospitals, Nigeria is estimated to have 4.25 million adults aged 40 years with severe eye diseases or blindness in which cataract is amongst the leading cause and with over 223 million people in Nigeria, this accounts for one third of the population thereby poses as a public health risk.
Sunlight Exposure

A new study by the National Eye Institute (NIH) emphasizes that years of chronic sunlight exposure can increase the risk of cataract and this resonates with the data from an independent study in Nigeria which shows that over 600 people have operable cataract in South Western Nigeria.
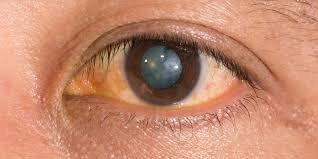
Cataract is a clouding of the lens of the eye which is typically clear. People with cataracts see through cloudy lenses which is like looking through a frosty or fogged-up window.
Symptoms of cataract include; clouded, blurred or dim vision, trouble seeing at night, sensitivity to light and glare and double vision in one eye.
The NIH researchers explain that sunlight can lead to cataract through a process called oxidative stress, which refers to the harmful chemical reactions that occur when our cells consume oxygen and other fuels to produce energy which is an unfortunate way of living.
Seriousness of the Issue

Further, the study suggest that UV light can damage lens protein in a distinct way called glycation that is typically seen in cataract and in cells damaged by oxidative stress and a joint estimate from International Labour Organization (ILO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) underscores the seriousness of the issue showing that over 1.6 billion people working under the age of 15 years or older were exposed to solar ultraviolet radiation in 2019 which resulted to health complications and contributed to over 19000 deaths.

In Nigeria, there’s an increase in outdoor work activities such as motorcycle drivers, farmers, prolonged screen time workers, that’s, remote workers due to the high cost transportation and fuel subsidy removal, this states the importance and urgent need of addressing prolonged sunlight.
Anya Kalu, Ophthalmologist
Africa Health Report (AHR) spoke to Dr.Anya Kalu. An eye specialist and leading ophthalmologist and phaco surgeon in an interview who affirmed that prolonged sunlight exposure can lead to the development of cataracts especially when UV radiation is being absorbed. That’s, when the eyes are exposed to UV radiation from sunlight, the cornea, lens and other ocular structures absorb this radiation.
Further, prolonged sunlight can lead to oxidative stress. This is when the absorbed UV radiation leads to generative oxygen species (ROS) and free radical within the lens of the eyes which can cause damage to the lens protein and cells.
Furthermore, prolonged sunlight can cause protein denaturation and gradual progression. This is when UV-induced oxidative stress causes denaturation, aggregation of lens proteins which leads to development of opacities in the lens, which is the defining characteristics of cataracts while gradual progression occurs when the damaged lens proteins accumulate overtime with prolonged UV exposure aiding to gradual development of cataracts.
Dr Kalu emphasizes that increased factors like age, genetics and other lifestyle habits such as smoking can increase cataract formation but its UV exposure is a paramount factor that contributes to cataract and it’s important to note that this takes years but the severity depends on the amount of UV exposure.
Kalu states that cataract is an economic burden and a public health burden. This is depicted in healthcare and indirect cost because treatment of cataract, including surgery and related medical expenses, represents substantial financial burdens including costs associated with cataracts such as transportation and loss of wages can add to the overall economic burden.
Impair Vision
The global impact and loss of productivity as a result of cataract. cataract as a leading cause of blindness worldwide can impair vision and reduce ability of individuals to work.
The public health burden of cataract includes;
vision impairment: Cataracts are the leading cause of vision impairment and blindness globally, affecting the quality of life and independence of individuals.
*Increased risk of accidents: Reduced vision due to cataracts can increase the risk of accidents, such as falls, and can also impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities safely.
* Burden on healthcare systems: The management of cataracts, including surgical procedures and postoperative care, places a significant demand on healthcare resources, straining the capacity of healthcare systems, especially in resource-limited settings.
*Societal impact: Vision impairment due to cataracts can lead to social isolation, reduced participation in community activities, and increased dependence on caregivers, affecting the overall well-being of individuals and their families.
*Equity issues: Lack of access to affordable cataract surgery disproportionately affects populations in low- and middle-income countries, contributing to health and socioeconomic disparities.
Recommendation and Prevention Cataract
Anya recommended that best to address cataract is through a multifaceted approach which includes, access to affordable and high-quality cataract surgical services, promoting early detection and implementing preventive strategies to reduce the risk of cataract development.
This also includes combined public awareness, early detection, improved access to treatment, and research-driven preventive strategies, the prevalence of cataracts can be minimized, contributing to better eye health and quality of life for individuals and communities worldwide.
The best way to prevent UV exposure is through, the use of UV-blocking sunglasses, hats, and other protective gear when exposed to sunlight and promoting the importance of protecting the eyes from prolonged UV exposure while educating the public about the link between UV exposure and cataract development.
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications:
– Promote a diet rich in antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, carotenoids, and omega-3 fatty acids, which can help mitigate oxidative stress and reduce the risk of cataract development.
– Encourage smoking cessation, as smoking is a risk factor for cataracts.
– Promote regular physical activity, as it may help reduce the risk of cataract formation.
Early Detection And Screening:
– Implement comprehensive eye health programs with regular eye examinations to detect cataracts in their early stages.
– Encourage regular eye check-ups, especially for populations at higher risk, such as the elderly or those with diabetes.
– Develop cost-effective screening and diagnostic tools to improve access to cataract detection, especially in underserved communities.
Improving Access to Cataract Surgery:
– Increase the availability and affordability of cataract surgical services, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
– Train and support a sufficient number of skilled ophthalmologists and eye care professionals to perform high-quality cataract surgeries.
– Explore innovative delivery models, such as mobile eye care units and telemedicine, to reach remote and underserved populations.
Preventive research and policy interventions:
– Invest in research to better understand the underlying mechanisms of cataract development and explore new preventive strategies.
– Develop and implement evidence-based policies and regulations to promote eye health and reduce the risk factors for cataracts.
– Collaborate with international organizations and governments to prioritize cataract prevention and control as a public health agenda.